Product Description
CHEVRON ( Patterned ) BELT
Product property
Chevron (patterned) conveyor belt is composed of belt carcass and pattern. The shape and height (dept) of patterns is subject to the material it conveys and the angle of the machine. On the surface of the belt there is a part higher than the belt body. We call it chevron or pattern.
Application
Chevron (patterned) conveyor belt mainly conveys powder, granulated, and small lump materials at the inclination of no more than 45º. It can also convey packaged material.
Some different chevron types are available, as below:
Production Procedure
1. Raw Material
2. Rubber Smelting and Shaping, Vulcanization
3. Quality Control, Packing and Loading
FAQ
Q1. Can I have a sample order?
Yes, any sample order is welcome to know the quality of our products.
Q2. What about the lead time of the sample or the final order?
2-5 days for normal sample.
20-30 days for a formal order.
Q3. How much is the widest conveyor belt you can produce.
2.5meters is the widest belt we can produce now.
Q4. Is it possible to print our logo or brand on the belt?
Yes, we can print your logo or design on the belt after receipt of your formal authorization letter of the logo or your brand.
Q5. Do you offer the guarantee for your product?
Yes, usually we offer 1 year warranty for all of our products.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | EP200 |
|---|---|
| Material: | Rubber |
| Inside Material: | Polyester |
| Feature: | Tear-Resistant, Wear-Resistant |
| Tensile Strength: | Strong |
| Cover Rubber: | 15MPa, 18MPa, 20MPa |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the cost considerations associated with using V-belts in power transmission?
When considering the use of V-belts in power transmission applications, several cost factors should be taken into account. Here are the key cost considerations associated with using V-belts:
- Initial Cost:
- Installation Cost:
- Maintenance Cost:
- Energy Efficiency:
- Replacement and Downtime Costs:
- Overall System Efficiency:
The initial cost of V-belts includes the purchase price of the belts themselves. V-belts are generally cost-effective compared to other power transmission options such as gears or chains. However, the specific cost can vary depending on factors such as belt type, size, and brand.
The installation cost involves the labor and time required to install the V-belts in the power transmission system. Compared to more complex power transmission systems, V-belts are relatively easy to install, requiring minimal specialized tools or expertise. This can result in lower installation costs.
V-belts generally require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Maintenance activities such as belt tensioning, alignment checks, and periodic replacements contribute to the overall maintenance cost. However, compared to other power transmission systems, V-belts often have lower maintenance costs due to their simplicity.
V-belts offer good energy efficiency, as they typically have low friction losses during power transmission. This can result in lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs over time. Choosing high-quality V-belts with low slip and efficient power transfer characteristics can further enhance energy efficiency.
Over time, V-belts will wear out and require replacement. The frequency of belt replacements will depend on factors such as operating conditions, maintenance practices, and belt quality. Planned belt replacements can help minimize unexpected downtime and associated costs. However, unplanned belt failures can lead to costly downtime, lost production, and potential damage to other system components.
The efficiency of the entire power transmission system should be considered when evaluating costs. While V-belts themselves are relatively efficient, the overall system efficiency can be influenced by factors such as pulley design, alignment, and load conditions. A well-designed and properly maintained V-belt drive system can optimize efficiency and reduce long-term operating costs.
By considering these cost considerations associated with using V-belts in power transmission, you can make informed decisions about the selection, installation, and maintenance of V-belt drive systems to achieve a balance between upfront costs and long-term operational efficiency.

What are the key differences between V-belts and other types of power transmission belts?
V-belts are a popular type of power transmission belts, but they differ from other types of belts in terms of design, construction, and specific applications. Here are the key differences:
1. Belt Profile:
V-belts have a trapezoidal or V-shaped cross-sectional profile, which gives them their name. This profile allows the belts to fit securely into V-shaped pulleys, providing effective power transmission and grip. Other types of belts, such as flat belts or timing belts, have different profiles suited for specific applications.
2. Power Transmission Method:
V-belts transmit power through frictional forces between the belt and the pulleys. As the belt wraps around the pulleys, the friction between the belt and the pulley surfaces allows the transfer of torque and power. In contrast, other belts, like timing belts or chain drives, use toothed profiles or interlocking mechanisms to transmit power, providing precise synchronization and higher torque transmission.
3. Load Capacity:
V-belts are designed to handle moderate to high loads, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, certain applications with heavier loads may require specialized heavy-duty V-belts or alternative belt types, such as synchronous belts or chain drives, which offer higher load-carrying capacities.
4. Speed Range:
V-belts are suitable for a broad speed range, but their limitations may vary depending on the specific design, material, and construction. Traditional V-belts may have speed limitations at extremely high speeds due to centrifugal forces and heat generation. High-speed V-belts or narrow V-belts are available for applications that require higher speeds. In contrast, timing belts and synchronous belts are designed for precise speed control and are commonly used in applications with strict speed requirements.
5. Tensioning and Maintenance:
V-belts require periodic tensioning to maintain proper grip and power transmission efficiency. Tensioning is typically achieved through manual adjustment or automatic tensioners. Other types of belts, such as timing belts or chain drives, often have fixed tensioning systems and require less frequent maintenance.
6. Noise and Vibration:
V-belts generally operate with lower noise and vibration levels compared to other types of belts, such as chain drives. The design and frictional nature of V-belts contribute to smoother operation and reduced noise generation, making them suitable for applications where noise and vibration control is important.
7. Applications:
V-belts are widely used in various applications, including industrial machinery, automotive systems, HVAC systems, and power transmission in general. They are versatile and can accommodate different power requirements. Other belt types, such as timing belts, are commonly used in precision positioning, robotics, or applications that require synchronous motion.
Overall, V-belts offer reliable and cost-effective power transmission for a wide range of applications. However, the selection of the appropriate belt type depends on factors such as load requirements, speed range, precision, noise considerations, and specific application needs.

How do you measure and select the right size of V-belt for a specific application?
When selecting the right size of V-belt for a specific application, it is important to consider factors such as the pulley diameters, center distance between the pulleys, power requirements, and the desired operating speed. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to measure and select the appropriate V-belt size:
- Identify the pulley diameters: Measure the diameter of both the driving and driven pulleys. Make sure to measure the diameter at the highest point of the pulley groove where the belt rides.
- Determine the center distance: Measure the distance between the center points of the driving and driven pulleys. This is the center distance and it plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate V-belt length.
- Calculate the pitch diameter: The pitch diameter is the effective diameter where the belt contacts the pulley. It can be calculated using the following formula: Pitch Diameter = (Driving Pulley Diameter + Driven Pulley Diameter) / 2.
- Consider the power requirements: Determine the amount of power that needs to be transmitted by the V-belt. This can be in the form of horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or engineering specifications to ensure the selected V-belt can handle the required power.
- Choose the appropriate V-belt type: Based on the calculated pitch diameter, center distance, and power requirements, select the type of V-belt that is suitable for the specific application. Consider factors such as load capacity, speed capability, and environmental conditions.
- Refer to V-belt manufacturer’s catalogs: Consult the manufacturer’s catalogs or online resources to find the available V-belt sizes and corresponding part numbers. Cross-reference the calculated parameters with the provided charts or tables to identify the appropriate V-belt size.
- Verify the selection: Double-check the selected V-belt size against the calculated parameters to ensure accuracy. If possible, consult with a technical expert or the manufacturer’s support team to validate the selection.
It is important to note that V-belt sizes are standardized and typically follow specific designations, such as the Classical V-belt designation (e.g., A, B, C, D) or the metric designation (e.g., SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC). These designations indicate different belt widths and lengths.
In summary, measuring and selecting the right size of V-belt for a specific application involves identifying the pulley diameters, determining the center distance, calculating the pitch diameter, considering the power requirements, choosing the appropriate V-belt type, referring to manufacturer’s catalogs, and verifying the selection. Following these steps will help ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the V-belt in the intended application.


editor by CX 2024-05-03
China OEM Synchronous Timing Cogged Industrial Rubber Raw Edged PU PVC Wrapped Banded Auto Motorcycle Transmission Tooth Drive Ribbed Poly Power V Belt example of wheel and axle
Product Description
Product Description
Raw materials
Belt: High-quality neoprene (CR)as the main raw materials( imported from Japan)
Skeleton materials: Glass Fiber(imported from Janpan)
Tooth surface: Nylon 66 high
Characteristics
strange anti-cracking properties,
CZPT excellent performance,
anti-aging,
heat resistance,
oil resistance,
abrasion-resistant
Features:
With synchronous belt drive is the use of tooth and tooth meshing with the impetus to pass a new type of transmission mode. With accurate synchronous transmission function, do not need lubrication and no slip, no pollution, less noise, transmission efficiency of 0.98, the speed ratio range up to 1: 10, allowing, wire speed up to 50 m / s, the transmission rate from several hundred watts to the hundreds of kilowatts, suitable for multi-axis drive. Neoprene synchronous belt widely used in the textile, automobile, chemical fiber, tobacco, paper, printing, chemical mechanical equipment; In recent years, mining and metallurgy, iron and steel machinery, medical equipment demand is growing.
| T type Industrial Timing Belt |
||||
| Type | Pitch Pb (mm) |
Tooth height ht (mm) |
Belt thickness hs (mm) |
Angle β ° |
| MXL | 2.032 | 0.51 | 1.14 | 40 |
| XL | 5.080 | 1.27 | 2.30 | 50 |
| L | 9.525 | 1.91 | 3.60 | 40 |
| H | 12.70 | 2.29 | 4.30 | 40 |
| XH | 22.225 | 6.35 | 11.20 | 40 |
| XXH | 31.750 | 9.53 | 15.70 | 40 |
| T2.5 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 1.30 | 40 |
| T5 | 5 | 1.20 | 2.20 | 40 |
| T10 | 10 | 2.50 | 4.50 | 40 |
| T20 | 20 | 5.00 | 8.00 | 40 |
| AT5 | 5 | 1.20 | 2.70 | 50 |
| AT10 | 10 | 2.50 | 5.00 | 50 |
| AT20 | 20 | 5.00 | 8.00 | 50 |
| Type | Pitch Pb(mm) | Tooth height ht(mm) | Belt thickness hs(mm) | Angle β° |
| HTD | 2M | 2 | 0.75 | 1.36 |
| 3M | 3 | 1.17 | 2.4 | |
| 5M | 5 | 2.06 | 3.8 | |
| 8M | 8 | 3.36 | 6.00 | |
| 14M | 14 | 6.02 | 10.00 | |
| 20M | 20 | 8.4 | 13.20 | |
| STPD/STS | S2M | 2 | 0.76 | 1.36 |
| S3M | 3 | 1.14 | 2.20 | |
| S4.5M | 4.5 | 1.71 | 2.81 | |
| S5M | 5 | 1.91 | 3.4 | |
| S8M | 8 | 3.05 | 5.3 | |
| S14M | 14 | 5.3 | 10.2 | |
| RPP/HPPD | 2M | 2 | 0.76 | 1.36 |
| 3M | 3 | 1.15 | 1.9 | |
| 5M | 5 | 1.95 | 3.5 | |
| 8M | 8 | 3.2 | 5.5 | |
| 14M | 14 | 6.00 | 10 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Auto Belt |
|---|---|
| Material: | Rubber |
| Certification: | ISO, DIN, JIS |
| Automatic: | Automatic |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Condition: | New |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any alternatives to V-belts for power transmission applications?
Yes, there are several alternatives to V-belts for power transmission applications. These alternatives offer different advantages and may be suitable for specific requirements. Here are some commonly used alternatives:
- Synchronous Belts:
- Flat Belts:
- V-Ribbed Belts:
- Chain Drives:
- Gear Drives:
- Direct Coupling:
Synchronous belts, also known as timing belts, are toothed belts that provide precise and synchronous power transmission. They have teeth on the inner side that mesh with corresponding grooves on the pulleys, eliminating slippage and ensuring accurate power transfer. Synchronous belts are commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, high torque transmission, or low maintenance.
Flat belts are thin, flexible belts that transmit power by friction between the belt and the pulleys. They offer a simple and cost-effective solution for power transmission. Flat belts are available in various materials, such as rubber, leather, or fabric-reinforced synthetic materials. They are suitable for applications with moderate power requirements and can be used in both light-duty and heavy-duty applications.
V-ribbed belts, also known as multi-rib belts or serpentine belts, are similar to V-belts but have a different cross-sectional shape. They have a flat or shallow V-shaped profile with ribs on the inner side, which engage with corresponding grooves on the pulleys. V-ribbed belts offer higher power transmission capacity and reduced slip compared to standard V-belts. They are commonly used in automotive applications, such as engine accessory drives.
Chain drives use a series of interconnected links to transmit power. They are known for their high strength, durability, and ability to handle heavy loads. Chain drives are commonly used in applications that require high torque transmission, such as industrial machinery, motorcycles, or bicycles. However, chain drives require periodic lubrication and maintenance to ensure proper operation.
Gear drives utilize interlocking gears to transmit power. They offer high efficiency, precise power transmission, and the ability to transmit large amounts of torque. Gear drives are commonly used in applications that require high precision, such as robotics, machine tools, or automotive transmissions. However, they can be more complex and expensive compared to belt drives.
In some cases, power transmission applications may utilize direct coupling, where the motor shaft is directly connected to the driven equipment without the use of belts or other intermediate components. Direct coupling offers high efficiency, compactness, and eliminates the need for belt maintenance. It is commonly used in applications with high torque requirements or where precise alignment is critical.
The choice of the alternative to V-belts depends on various factors, including the specific power transmission requirements, space limitations, cost considerations, maintenance needs, and the desired level of precision. It is important to evaluate these factors and consult with experts to select the most suitable alternative for a particular application.
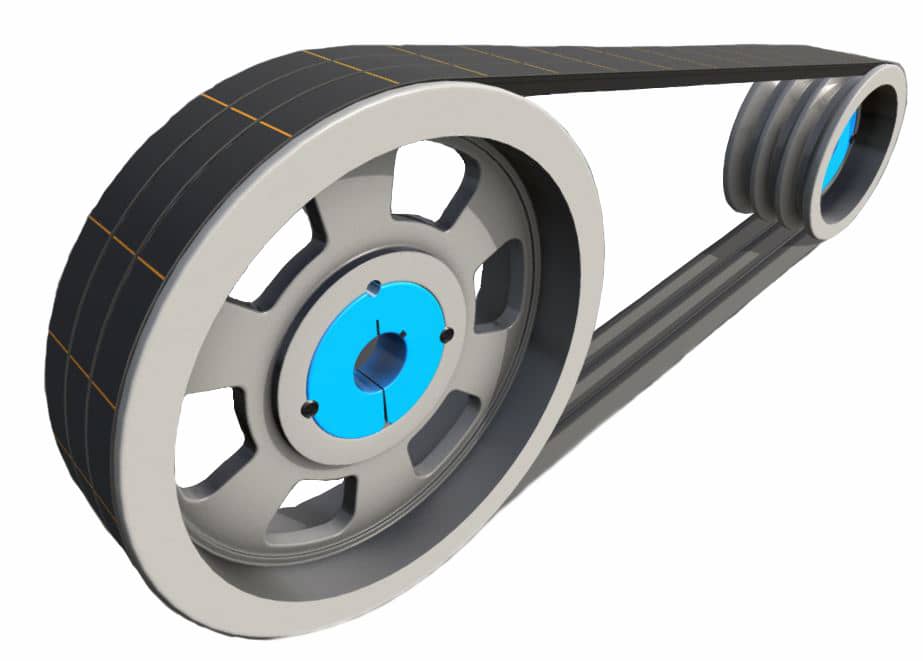
How do you troubleshoot common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing?
Troubleshooting common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing, is essential to maintain the proper operation and efficiency of the belt drive system. Here are some troubleshooting steps to address these issues:
- Slipping:
- Check the belt tension: Insufficient tension is a common cause of slipping. Ensure that the V-belt is properly tensioned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Adjust the tension by using the appropriate tensioning method or tools.
- Inspect for wear or damage: Examine the V-belt for signs of wear, cracks, fraying, or other damage. A worn-out belt may not provide adequate grip and can lead to slipping. Replace the belt if necessary.
- Check pulley alignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to slip. Verify that the pulleys are properly aligned both parallel and angularly. Adjust the pulley positions if misalignment is detected.
- Assess pulley condition: Worn or damaged pulleys can contribute to belt slipping. Inspect the pulleys for wear, rough surfaces, or damage. If needed, replace the pulleys to ensure proper belt engagement.
- Verify the load and application: Excessive loads or improper application can cause the belt to slip. Ensure that the belt drive system is designed and rated for the specific load requirements.
- Squealing:
- Check belt tension: Insufficient or excessive belt tension can lead to squealing. Adjust the tension to the recommended range specified by the manufacturer.
- Inspect for wear or contamination: Check the V-belt for signs of wear, glazing, or contamination. Worn or contaminated belts may produce squealing noises. Replace the belt if necessary and eliminate any contamination from the belt or pulleys.
- Examine pulley condition: Damaged or worn pulleys can create noise. Inspect the pulleys for wear, damage, or rough surfaces. Replace any worn or damaged pulleys.
- Verify pulley alignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to run at an angle, resulting in noise. Ensure that the pulleys are correctly aligned both parallel and angularly. Adjust the pulley positions if misalignment is detected.
- Check for belt glazing: Belt glazing occurs when the belt’s contact surface becomes smooth and glossy, reducing traction. If glazing is present, roughen the belt’s surface with fine sandpaper or replace the belt if necessary.
- Assess environmental factors: Environmental conditions, such as excessive heat or humidity, can affect belt performance. Ensure that the belt drive system operates within the recommended temperature and humidity ranges.
Slipping occurs when the V-belt fails to maintain proper traction with the pulleys, resulting in reduced power transmission and potential belt wear. To troubleshoot slipping issues:
Squealing noises from V-belts are often caused by vibrations, misalignment, or improper tension. To troubleshoot squealing issues:
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can identify and address common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing. Regular maintenance, proper tensioning, and alignment are crucial for ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of the belt drive system.

What is a V-belt and how does it work?
A V-belt, also known as a Vee belt or a wedge belt, is a type of power transmission belt that is commonly used in various industrial applications. It is called a V-belt because of its trapezoidal cross-sectional shape, resembling the letter “V.”
The primary purpose of a V-belt is to transmit power between two rotating shafts. It does this by wrapping around the pulleys or sheaves on the shafts and creating frictional forces between the belt and the pulleys. The friction generated between the belt and the pulleys allows the belt to transfer torque from the driving pulley to the driven pulley.
The V-belt’s design provides several advantages for power transmission:
- High friction: The V-shaped cross-section of the belt increases the contact area with the pulleys, resulting in high frictional forces. This allows for effective power transmission even in applications with high torque or heavy loads.
- Belt wedging: When the V-belt is tensioned, it wedges itself deeper into the pulley grooves, enhancing the friction and preventing slippage between the belt and the pulleys. This feature is especially useful in applications where the driven pulley needs to rotate at a different speed than the driving pulley.
- Quiet operation: V-belts generally operate with less noise compared to other types of belts, such as flat belts. The V-shaped design helps to reduce vibrations and noise levels during power transmission.
- Simple installation: V-belts are relatively easy to install and replace. They can be quickly mounted on the pulleys without requiring extensive alignment procedures.
However, it’s important to note that V-belts have limitations as well. They are not suitable for applications that require precise speed control or when high-speed ratios are needed. In such cases, other power transmission methods like gear systems or synchronous belts may be more appropriate.
In summary, V-belts are commonly used power transmission belts that utilize frictional forces to transfer torque between rotating shafts. Their V-shaped design and high friction characteristics make them effective for various industrial applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-03
China wholesaler High Quality Wrapped V Belt Rubber V Belt with Factory Price Air Conditioner Belt ISO9001/ISO45001/Ts16949/ISO14001 Auto Spare Parts for KIA/Mazda/Toyota axle end caps
Product Description
Transco Belt offers high-quality wrapped V belts in China, designed for industrial machines
Product Description
The Classical V Belt, also known as a wrapped v belt, is a circular transmission belt with a trapezoidal cross-section that falls under the V-belt category.
This type of belt is popular and widely utilized in various industries due to its ease of installation, compact size, high transmission efficiency, and minimal noise output. It is ideal for power transmission applications with small center distances and high transmission ratios, often found in textile machinery, machine tools, and general power transmission systems.
Specification
Li= Inner Circle Length
La= Outer Circle Length
Ld/Lw/Lp=Pitch Length
(Baseline Length)
| Model | Top Width | Height | Angle | Length range-MM |
| Z/M/O | 10 | 6 | 40° | 381—-5000 |
| A | 13 | 8 | 40° | 381—-10000 |
| B | 17 | 11 | 40° | 508—-18000 |
| C | 22 | 14 | 40° | 635—-18000 |
| D | 32 | 19 | 40° | 762—-16000 |
| E | 38 | 23 | 40° | 1016—-15000 |
| F | 50 | 30 | 40° | 1016—-10000 |
Transco V-belt features:
A:Transco uses the abrasion-resistant and flexible cover fabric offers a strong grip on sheaves to reduce slippage during operation.
Top cover constructed from multiple strands of yarn, the rubber treatment enhances adhesion, protects against the elements, and prevents static build-up in challenging usage.
B:The top rubber binds the tensile cord, fabric cover, and compression rubber to prevent separation of the belt components during operation.
C:Transco provides high quality Tensile cord and these cords are twisted in different configurations to match load applications and are pre-stretched before belt assembly to stabilize length and minimize stretching during operation
D:Transco uses high-quality production formulas to provide V belts that are resistant to flex cracking and compression fatigue.
Advantages of Transco belts:
1. Oil, heat, CZPT and abrasion resistant.
2. High loads, low elongation and long service life, high flexibility.
3. Temperature resistance: -45ºC-+70ºC
4. Oil resistant, anti-static per ISO1813.
5. Standards: ISO4184, DIN2215, RMA.
Production process
Our certificate
Packing & Delivery
Our business partner
Transco Belt has long-term cooperative relationships with many famous companies, and with a philosophy centered on “Connecting everything with Transmission and Science” we are dedicated to assisting our customers in achieving efficient operations, extended service life, and superior product quality.
Company Profile
HangZhou Transco Belt Co., Ltd. is a reputable rubber belt and conveyor belt manufacturing company based in HangZhou, ZHangZhoug Province, China. With a focus on designing, manufacturing, marketing, and installing a diverse range of belts, our company has established a modern production line equipped with advanced testing and controlling laboratories. We boast a professional team dedicated to research and development, production, sales, and service. As a leading manufacturer and exporter in China, Transco Belt offers a comprehensive range of rubber V belts and conveyor belts, catering to various industries worldwide.
FAQ
Q1. Are you a manufactuer?
Yes, we have been producing V belts for more than 20 years!
Welcome to visit our factory!
Q2. What about the delivery time?
1) 1–2 days for sample
2) 10~30 days according to order quantity
Q3. How to pay?
1) T/T , L/C,D/P through bank account
2) Select global pay by made in china
Q4. How about package?
1)Cartons packing.
2)We also can provide wooden pallets, iron pallets, frame packaging or other customized packaging
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyer Equipment, Packaging Machinery, Motorcycle, Mining Equipment, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
| Feature: | Flame-Retardant, Anti-Static, Oil-Resistant, Heat-Resistant, Wear-Resistant, Acid-Resistant, High Temperature-Resistance |
| Tensile Strength: | Strong |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Type: | V Belt |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are there any alternatives to V-belts for power transmission applications?
Yes, there are several alternatives to V-belts for power transmission applications. These alternatives offer different advantages and may be suitable for specific requirements. Here are some commonly used alternatives:
- Synchronous Belts:
- Flat Belts:
- V-Ribbed Belts:
- Chain Drives:
- Gear Drives:
- Direct Coupling:
Synchronous belts, also known as timing belts, are toothed belts that provide precise and synchronous power transmission. They have teeth on the inner side that mesh with corresponding grooves on the pulleys, eliminating slippage and ensuring accurate power transfer. Synchronous belts are commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, high torque transmission, or low maintenance.
Flat belts are thin, flexible belts that transmit power by friction between the belt and the pulleys. They offer a simple and cost-effective solution for power transmission. Flat belts are available in various materials, such as rubber, leather, or fabric-reinforced synthetic materials. They are suitable for applications with moderate power requirements and can be used in both light-duty and heavy-duty applications.
V-ribbed belts, also known as multi-rib belts or serpentine belts, are similar to V-belts but have a different cross-sectional shape. They have a flat or shallow V-shaped profile with ribs on the inner side, which engage with corresponding grooves on the pulleys. V-ribbed belts offer higher power transmission capacity and reduced slip compared to standard V-belts. They are commonly used in automotive applications, such as engine accessory drives.
Chain drives use a series of interconnected links to transmit power. They are known for their high strength, durability, and ability to handle heavy loads. Chain drives are commonly used in applications that require high torque transmission, such as industrial machinery, motorcycles, or bicycles. However, chain drives require periodic lubrication and maintenance to ensure proper operation.
Gear drives utilize interlocking gears to transmit power. They offer high efficiency, precise power transmission, and the ability to transmit large amounts of torque. Gear drives are commonly used in applications that require high precision, such as robotics, machine tools, or automotive transmissions. However, they can be more complex and expensive compared to belt drives.
In some cases, power transmission applications may utilize direct coupling, where the motor shaft is directly connected to the driven equipment without the use of belts or other intermediate components. Direct coupling offers high efficiency, compactness, and eliminates the need for belt maintenance. It is commonly used in applications with high torque requirements or where precise alignment is critical.
The choice of the alternative to V-belts depends on various factors, including the specific power transmission requirements, space limitations, cost considerations, maintenance needs, and the desired level of precision. It is important to evaluate these factors and consult with experts to select the most suitable alternative for a particular application.

Are there any safety considerations when working with V-belts?
Working with V-belts involves certain safety considerations to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the belt drive system. Here are some important safety considerations when working with V-belts:
- Lockout/Tagout: Before performing any maintenance or adjustment on a belt drive system, it is crucial to follow proper lockout/tagout procedures. Lockout/tagout involves isolating the power source, de-energizing the equipment, and securing it with locks or tags to prevent unintentional startup or release of stored energy. This ensures the safety of personnel working on or near the V-belts.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with V-belts, appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn as per the specific tasks and potential hazards. This may include safety glasses, gloves, hearing protection, and protective clothing to safeguard against potential injury from flying debris, pinch points, or contact with rotating parts.
- Training and Familiarity: Ensure that personnel working with V-belts are adequately trained on safe work practices, including proper maintenance procedures, tensioning techniques, and the use of tools and equipment. Familiarity with the specific belt drive system and understanding the potential hazards associated with V-belts is essential for safe operation.
- Machine Guarding: Install appropriate machine guarding to prevent accidental contact with moving V-belts and exposed pulleys. Guards should be designed to prevent access to hazardous areas and comply with relevant safety regulations. Regularly inspect and maintain the guards to ensure their effectiveness.
- Tensioning and Adjustment: Follow proper procedures when tensioning or adjusting V-belts. Use the recommended tools and techniques specified by the manufacturer. Improper tensioning can lead to belt slippage, increased wear, and potential accidents. Avoid working near or reaching into the belt drive system while it is in operation.
- Proper Lifting and Handling: V-belts can be heavy and awkward to handle, especially in larger sizes. When lifting or handling V-belts, use proper lifting techniques and equipment to prevent strains or injuries. Avoid placing excessive stress on the belts during installation or removal.
- Maintaining Cleanliness: Keep the work area clean and free from debris, oil, or other contaminants that may affect traction or create slip hazards. Clean up any spills promptly and use appropriate cleaning methods to avoid slipping or tripping accidents.
- Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and specifications for the installation, tensioning, maintenance, and replacement of V-belts. Manufacturers provide valuable information on safe operating practices, recommended tension ranges, load capacities, and other relevant safety considerations specific to their V-belt products.
By following these safety considerations when working with V-belts, you can help mitigate potential hazards, reduce the risk of accidents, and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the belt drive system.

How do you measure and select the right size of V-belt for a specific application?
When selecting the right size of V-belt for a specific application, it is important to consider factors such as the pulley diameters, center distance between the pulleys, power requirements, and the desired operating speed. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to measure and select the appropriate V-belt size:
- Identify the pulley diameters: Measure the diameter of both the driving and driven pulleys. Make sure to measure the diameter at the highest point of the pulley groove where the belt rides.
- Determine the center distance: Measure the distance between the center points of the driving and driven pulleys. This is the center distance and it plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate V-belt length.
- Calculate the pitch diameter: The pitch diameter is the effective diameter where the belt contacts the pulley. It can be calculated using the following formula: Pitch Diameter = (Driving Pulley Diameter + Driven Pulley Diameter) / 2.
- Consider the power requirements: Determine the amount of power that needs to be transmitted by the V-belt. This can be in the form of horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or engineering specifications to ensure the selected V-belt can handle the required power.
- Choose the appropriate V-belt type: Based on the calculated pitch diameter, center distance, and power requirements, select the type of V-belt that is suitable for the specific application. Consider factors such as load capacity, speed capability, and environmental conditions.
- Refer to V-belt manufacturer’s catalogs: Consult the manufacturer’s catalogs or online resources to find the available V-belt sizes and corresponding part numbers. Cross-reference the calculated parameters with the provided charts or tables to identify the appropriate V-belt size.
- Verify the selection: Double-check the selected V-belt size against the calculated parameters to ensure accuracy. If possible, consult with a technical expert or the manufacturer’s support team to validate the selection.
It is important to note that V-belt sizes are standardized and typically follow specific designations, such as the Classical V-belt designation (e.g., A, B, C, D) or the metric designation (e.g., SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC). These designations indicate different belt widths and lengths.
In summary, measuring and selecting the right size of V-belt for a specific application involves identifying the pulley diameters, determining the center distance, calculating the pitch diameter, considering the power requirements, choosing the appropriate V-belt type, referring to manufacturer’s catalogs, and verifying the selection. Following these steps will help ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the V-belt in the intended application.


editor by CX 2024-05-03
China wholesaler Xpa832 Toothed Triangle Belts/Super Tx Vextra V-Belts/High Temperature Timing Belts axle bearing
Product Description
XPA832 Toothed Triangle Belts/Super TX Vextra V-Belts/High Temperature Timing Belts
Specification
There’s 556 pcs of XPA832 belts are available in stock now, you can send me an email or Skype messages or What’sapp
messages to contact me if want to order or consult information of XPA832 belts, the prompt response, competitive prices,
superior quality and service are waiting for you.
The detailed technical sheet of XPA832 belts as follows:
| Model | XPA832 | |
| Type | V-belts | |
| Description | Toothed Triangle Belts/Super TX Vextra Belts/High Temperature Timing Belts | |
| mass | 0.15 KG | |
| Service | Neutral/OEM/As per your request | |
| Package | Carton Box | |
| Stock Qty | 556 pcs | |
| Country of Origin | USA/Germany/Japan | |
| HS Code | 4571390000 | |
Wanna more information of XPA832 beltss, or still sourcing any other bearings, linear blocks/rails, industrial V-belts or sparg plugs,
just contact me now.
In addition, the following V-belts are available now, pls feel free to let me know if you’re interested in it:
XPA series of toothed V-belt
XPA732 , XPA747 , XPA757 , XPA770 , XPA782 , XPA800 , XPA810 , XPA820 , XPA832 ,XPA850 , XPA857 , XPA882 , XPA900 , XPA907 , XPA925 , XPA932 , XPA950 , XPA957 ,XPA975 , XPA982 , XPA1000 , XPA1007 , XPA1030 , XPA1060 , XPA1080 , XPA1090 ,XPA1107 , XPA1120 , XPA1132 , XPA1140 , XPA1150 , XPA1157 , XPA1180 , XPA1207 , XPA1215 , XPA1232 , XPA1250 , XPA1272 , XPA1282 , XPA1307 , XPA1320 , XPA1332 , XPA1357 , XPA1382 , XPA1400 , XPA1407 , XPA1432 , XPA1450 , XPA1457 , XPA1482 , XPA1500 , XPA1500 , XPA1507 , XPA1532 , XPA1550 , XPA1557 , XPA1582 , XPA1600 , XPA1607 , XPA1632 , XPA1650 , XPA1657 , XPA1682 , XPA1700 , XPA1732 , XPA1750 , XPA1757 , XPA1782 , XPA1800 , XPA1807 , XPA1832 , XPA1850 , XPA1857 , XPA1882 , XPA1900 , XPA1907 , XPA1932 , XPA1950 , XPA1957 , XPA1982 , XPA2000 , XPA2032 , XPA2060 , XPA2082 , XPA2120 , XPA2132 , XPA2182 , XPA2240 , XPA2282 , XPA2300 , XPA2332 , XPA2360 , XPA2382 , XPA2430 , XPA2482 , XPA2500 , XPA2532 , XPA2582 , XPA2607 , XPA2632 , XPA2650 , XPA2682 , XPA2732 , XPA2782 , XPA2800 , XPA2832 , XPA2847 , XPA2882 , XPA2900 , XPA2932 , XPA2982 , XPA3000 , XPA3150 , XPA3350 , XPA3550
XPB series of toothed V-belt
XPB1130 , XPB1180 , XPB1230 , XPB1250 , XPB1260 , XPB1280 , XPB1320 , XPB1340 , XPB1360 , XPB1380 , XPB1400 , XPB1410 , XPB1430 , XPB1460 , XPB1480 , XPB1500 , XPB1510 , XPB1540 , XPB1590 , XPB1600 , XPB1640 , XPB1660 , XPB1690 , XPB1700 , XPB1720 , XPB1740 , XPB1800 , XPB1840 , XPB1870 , XPB1900 , XPB2000 , XPB2571 , XPB2040 , XPB2100 , XPB2120 , XPB2150 , XPB2160 , XPB2170 , XPB2220 , XPB2240 , XPB2280 , XPB2350 , XPB2360 , XPB2380 , XPB2410 , XPB2430 , XPB2500 , XPB2530 , XPB2600 , XPB2650 , XPB2680 , XPB2730 , XPB2800 , XPB2840 , XPB2910 , XPB2990 , XPB3000 , XPB3110 , XPB3150 , XPB3170 , XPB3340 , XPB3550
XPC series of toothed V-belt
XPC2000, XPC2120, XPC2240, XPC2360, XPC2500 ,XPC2650, XPC2800XPC3000, XPC3150, XPC3350, XPC3550, XPC3750 ,XPC4000 ,XPC4250, XPC4500 XPC4750
XPZ series of toothed V-belt
XPZ560 ,XPZ612 ,XPZ621 ,XPZ630 ,XPZ637 ,XPZ662 ,XPZ670 ,XPZ687 ,XPZ710,XPZ722 ,XPZ730 ,XPZ737 ,XPZ750 ,XPZ760 ,XPZ762 ,XPZ772 ,XPZ787 ,XPZ800,XPZ812 ,XPZ825 ,XPZ837 ,XPZ850 ,XPZ862 ,XPZ875 ,XPZ887 ,XPZ900 ,XPZ912,XPZ925 ,XPZ937 ,XPZ950 ,XPZ962 ,XPZ975 ,XPZ987 ,XPZ1000 ,XPZ1571 , XPZ1012 , XPZ1571 , XPZ1030 , XPZ1037 , XPZ1047 , XPZ1060 , XPZ1077 , XPZ1080 , XPZ1087 , XPZ1100 , XPZ1112 , XPZ1120 , XPZ1140 , XPZ1150 , XPZ1162 , XPZ1180 , XPZ1187 , XPZ1200 , XPZ1212 , XPZ1222 , XPZ1237 , XPZ1250 , XPZ1262 , XPZ1270 , XPZ1287 , XPZ1312 , XPZ1320 , XPZ1337 , XPZ1340 , XPZ1347 , XPZ1362 , XPZ1387 , XPZ1400 , XPZ1412 , XPZ1420 , XPZ1437 , XPZ1450 , XPZ1462 , XPZ1487 , XPZ1500 , XPZ1512 , XPZ1520 , XPZ1537 , XPZ1550 , XPZ1562 , XPZ1587 , XPZ1600 , XPZ1612 , XPZ1637 , XPZ1650 , XPZ1662 , XPZ1687 , XPZ1700 , XPZ1737 , XPZ1750 , XPZ1762 , XPZ1782 , XPZ1800 , XPZ1812 , XPZ1837 , XPZ1850 , XPZ1862 , XPZ1887 , XPZ1900 , XPZ1937 , XPZ1950 , XPZ1987 , XPZ2000 , XPZ2030 , XPZ2060 , XPZ2120 , XPZ2160 , XPZ2240 , XPZ2280 , XPZ2360 , XPZ2410 , XPZ2487 , XPZ2500 , XPZ2540 , XPZ2650 , XPZ2690 , XPZ2840 , XPZ3000 , XPZ3170 , XPZ3350 , XPZ3550
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyer Equipment, Packaging Machinery, Food Machinery, Marine, Mining Equipment |
| Feature: | Anti-Static, Oil-Resistant, Cold-Resistant, Corrosion-Resistant, Heat-Resistant, High Temperature-Resistance |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Are there any specific guidelines for aligning pulleys and V-belts?
Proper alignment between pulleys and V-belts is essential to ensure smooth operation, minimize wear, and maximize the efficiency of the belt drive system. Here are some specific guidelines for aligning pulleys and V-belts:
- Parallel Alignment:
- Angular Alignment:
- Alignment Tools:
- Adjustment Methods:
- Regular Inspections:
- Manufacturer Recommendations:
The pulleys should be aligned parallel to each other, meaning that the axes of the pulleys should be in the same plane. This ensures that the V-belt runs straight and evenly between the pulleys. Misalignment can cause the belt to run at an angle, leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency.
In addition to parallel alignment, the pulleys should be aligned angularly. This means that the pulley faces should be perpendicular to the belt’s direction of travel. Angular misalignment can cause the belt to twist and create uneven tension, resulting in increased wear and potential belt failure.
To achieve proper alignment, various alignment tools can be used, such as straightedges, laser alignment tools, or alignment software. These tools help in measuring and adjusting the alignment of pulleys, ensuring precise parallel and angular alignment.
To adjust the alignment of pulleys, different methods can be employed. Common adjustment methods include shimming, moving the pulley on its shaft, or using adjustable pulleys. The specific method depends on the type of pulley and the adjustment capabilities of the system.
Regular inspections are crucial to identify and correct any misalignment issues promptly. Inspect the pulleys visually and check for any signs of misalignment, such as uneven belt wear, belt tracking issues, or abnormal belt noise. If misalignment is detected, take corrective measures to realign the pulleys.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for pulley alignment. Manufacturers often provide specific alignment tolerances and recommendations for their products, considering factors such as belt type, load, and operating conditions. Follow these recommendations to ensure proper alignment and optimize the performance of the belt drive system.
By following these guidelines for aligning pulleys and V-belts, you can minimize wear, reduce the risk of belt failure, and maximize the efficiency and lifespan of the belt drive system.

What are the factors that affect the lifespan and efficiency of V-belts?
The lifespan and efficiency of V-belts can be influenced by several factors. Here are the key factors that can affect the performance of V-belts:
- Belt Tension:
- Belt Alignment:
- Belt Condition:
- Maintenance and Lubrication:
- Operating Conditions:
- Load and Application:
Proper belt tension is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of V-belts. Insufficient tension can cause slippage, while excessive tension can lead to excessive load on the belt and other components. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the correct tension range.
Poor belt alignment can cause uneven wear, increased friction, and reduced efficiency. Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to run at an angle, resulting in premature wear and potential failure. Regularly check and adjust the alignment of pulleys to ensure proper belt tracking.
The condition of the V-belt itself is a significant factor in its lifespan and efficiency. Regularly inspect the belt for signs of wear, cracks, fraying, or glazing. Replace worn-out or damaged belts promptly to avoid further issues.
Proper maintenance and lubrication can significantly extend the lifespan of V-belts. Adequate lubrication reduces friction and heat buildup, which helps to prevent premature wear and cracking. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use the appropriate lubricant.
Operating conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals or contaminants, can affect the performance of V-belts. Extreme temperatures can cause the belt material to deteriorate, while exposure to chemicals or contaminants can lead to belt degradation. Ensure that the operating conditions are within the recommended range for the specific V-belt.
The load and application requirements also impact the lifespan and efficiency of V-belts. Excessive loads or improper application can cause excessive stress on the belt, leading to premature failure. Ensure that the V-belt is appropriately sized and rated for the specific load and application.
By considering these factors and implementing proper maintenance practices, such as regular inspections, correct tensioning, alignment checks, and appropriate lubrication, you can maximize the lifespan and efficiency of V-belts in your applications.

What are the advantages of using V-belts in power transmission systems?
V-belts offer several advantages when used in power transmission systems:
- High friction: The V-shaped cross-section of the belt increases the contact area with the pulleys, resulting in high frictional forces. This allows for effective power transmission even in applications with high torque or heavy loads.
- Belt wedging: When the V-belt is tensioned, it wedges itself deeper into the pulley grooves, enhancing the friction and preventing slippage between the belt and the pulleys. This feature is especially useful in applications where the driven pulley needs to rotate at a different speed than the driving pulley.
- Quiet operation: V-belts generally operate with less noise compared to other types of belts, such as flat belts. The V-shaped design helps to reduce vibrations and noise levels during power transmission.
- Simple installation: V-belts are relatively easy to install and replace. They can be quickly mounted on the pulleys without requiring extensive alignment procedures.
- Cost-effective: V-belts are typically more affordable compared to other power transmission methods, such as gear systems or synchronous belts. This makes them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
- Flexibility: V-belts can accommodate misalignments and slight variations in pulley diameters. They can also operate in a wide range of temperature and humidity conditions, making them versatile for different environments.
- Energy efficiency: V-belts have relatively low energy losses during power transmission, resulting in efficient energy transfer between the driving and driven pulleys.
It’s important to note that while V-belts offer numerous advantages, they also have limitations. They are not suitable for applications that require precise speed control or when high-speed ratios are needed. In such cases, other power transmission methods may be more appropriate.
In conclusion, the advantages of using V-belts in power transmission systems include high friction, belt wedging, quiet operation, simple installation, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and energy efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-05-03
China high quality Xpb2910 Toothed V-Belts/Super Tx Vextra Belts electric rear axle kit
Product Description
XPB2910 Toothed V-belts/Super TX Vextra Belts
Specification
There’s 556 pcs of XPB2910 belts are available in stock now, you can send me an email or Skype messages or What’sapp
messages to contact me if want to order or consult information of XPB2910 belts, the prompt response, competitive prices,
superior quality and service are waiting for you.
The detailed technical sheet of XPB2910 belts as follows:
| Model | XPB2910 | |
| Type | V-belts | |
| Description | Toothed V-belts/Super TX Vextra Belts | |
| mass | 0.5 KG | |
| Service | Neutral/OEM/As per your request | |
| Package | Carton Box | |
| Stock Qty | 556 pcs | |
| Country of Origin | USA/Germany | |
| HS Code | 4571390000 | |
Wanna more information of XPB2910 beltss, or still sourcing any other bearings, linear blocks/rails, industrial V-belts or sparg plugs,
just contact me now.
In addition, the following V-belts are available now, pls feel free to let me know if you’re interested in it:
XPA series of toothed V-belt
XPA732 , XPA747 , XPA757 , XPA770 , XPA782 , XPA800 , XPA810 , XPA820 , XPA832 ,XPA850 , XPA857 , XPA882 , XPA900 , XPA907 , XPA925 , XPA932 , XPA950 , XPA957 ,XPA975 , XPA982 , XPA1000 , XPA1007 , XPA1030 , XPA1060 , XPA1080 , XPA1090 ,XPA1107 , XPA1120 , XPA1132 , XPA1140 , XPA1150 , XPA1157 , XPA1180 , XPA1207 , XPA1215 , XPA1232 , XPA1250 , XPA1272 , XPA1282 , XPA1307 , XPA1320 , XPA1332 , XPA1357 , XPA1382 , XPA1400 , XPA1407 , XPA1432 , XPA1450 , XPA1457 , XPA1482 , XPA1500 , XPA1500 , XPA1507 , XPA1532 , XPA1550 , XPA1557 , XPA1582 , XPA1600 , XPA1607 , XPA1632 , XPA1650 , XPA1657 , XPA1682 , XPA1700 , XPA1732 , XPA1750 , XPA1757 , XPA1782 , XPA1800 , XPA1807 , XPA1832 , XPA1850 , XPA1857 , XPA1882 , XPA1900 , XPA1907 , XPA1932 , XPA1950 , XPA1957 , XPA1982 , XPA2000 , XPA2032 , XPA2060 , XPA2082 , XPA2120 , XPA2132 , XPA2182 , XPA2240 , XPA2282 , XPA2300 , XPA2332 , XPA2360 , XPA2382 , XPA2430 , XPA2482 , XPA2500 , XPA2532 , XPA2582 , XPA2607 , XPA2632 , XPA2650 , XPA2682 , XPA2732 , XPA2782 , XPA2800 , XPA2832 , XPA2847 , XPA2882 , XPA2900 , XPA2932 , XPA2982 , XPA3000 , XPA3150 , XPA3350 , XPA3550
XPB series of toothed V-belt
XPB1130 , XPB1180 , XPB1230 , XPB1250 , XPB1260 , XPB1280 , XPB1320 , XPB1340 , XPB1360 , XPB1380 , XPB1400 , XPB1410 , XPB1430 , XPB1460 , XPB1480 , XPB1500 , XPB1510 , XPB1540 , XPB1590 , XPB1600 , XPB1640 , XPB1660 , XPB1690 , XPB1700 , XPB1720 , XPB1740 , XPB1800 , XPB1840 , XPB1870 , XPB1900 , XPB2000 , XPB2571 , XPB2040 , XPB2100 , XPB2120 , XPB2150 , XPB2160 , XPB2170 , XPB2220 , XPB2240 , XPB2280 , XPB2350 , XPB2360 , XPB2380 , XPB2410 , XPB2430 , XPB2500 , XPB2530 , XPB2600 , XPB2650 , XPB2680 , XPB2730 , XPB2800 , XPB2840 , XPB2910 , XPB2990 , XPB3000 , XPB3110 , XPB3150 , XPB3170 , XPB3340 , XPB3550
XPC series of toothed V-belt
XPC2000, XPC2120, XPC2240, XPC2360, XPC2500 ,XPC2650, XPC2800XPC3000, XPC3150, XPC3350, XPC3550, XPC3750 ,XPC4000 ,XPC4250, XPC4500 XPC4750
XPZ series of toothed V-belt
XPZ560 ,XPZ612 ,XPZ621 ,XPZ630 ,XPZ637 ,XPZ662 ,XPZ670 ,XPZ687 ,XPZ710,XPZ722 ,XPZ730 ,XPZ737 ,XPZ750 ,XPZ760 ,XPZ762 ,XPZ772 ,XPZ787 ,XPZ800,XPZ812 ,XPZ825 ,XPZ837 ,XPZ850 ,XPZ862 ,XPZ875 ,XPZ887 ,XPZ900 ,XPZ912,XPZ925 ,XPZ937 ,XPZ950 ,XPZ962 ,XPZ975 ,XPZ987 ,XPZ1000 ,XPZ1571 , XPZ1012 , XPZ1571 , XPZ1030 , XPZ1037 , XPZ1047 , XPZ1060 , XPZ1077 , XPZ1080 , XPZ1087 , XPZ1100 , XPZ1112 , XPZ1120 , XPZ1140 , XPZ1150 , XPZ1162 , XPZ1180 , XPZ1187 , XPZ1200 , XPZ1212 , XPZ1222 , XPZ1237 , XPZ1250 , XPZ1262 , XPZ1270 , XPZ1287 , XPZ1312 , XPZ1320 , XPZ1337 , XPZ1340 , XPZ1347 , XPZ1362 , XPZ1387 , XPZ1400 , XPZ1412 , XPZ1420 , XPZ1437 , XPZ1450 , XPZ1462 , XPZ1487 , XPZ1500 , XPZ1512 , XPZ1520 , XPZ1537 , XPZ1550 , XPZ1562 , XPZ1587 , XPZ1600 , XPZ1612 , XPZ1637 , XPZ1650 , XPZ1662 , XPZ1687 , XPZ1700 , XPZ1737 , XPZ1750 , XPZ1762 , XPZ1782 , XPZ1800 , XPZ1812 , XPZ1837 , XPZ1850 , XPZ1862 , XPZ1887 , XPZ1900 , XPZ1937 , XPZ1950 , XPZ1987 , XPZ2000 , XPZ2030 , XPZ2060 , XPZ2120 , XPZ2160 , XPZ2240 , XPZ2280 , XPZ2360 , XPZ2410 , XPZ2487 , XPZ2500 , XPZ2540 , XPZ2650 , XPZ2690 , XPZ2840 , XPZ3000 , XPZ3170 , XPZ3350 , XPZ3550
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyer Equipment, Packaging Machinery, Food Machinery, Marine, Mining Equipment |
| Feature: | Anti-Static, Oil-Resistant, Cold-Resistant, Corrosion-Resistant, Heat-Resistant, High Temperature-Resistance |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What are the key differences between standard V-belts and cogged V-belts?
Standard V-belts and cogged V-belts are two variations of V-belts that differ in their design and performance characteristics. Here are the key differences between these two types of belts:
- Design:
- Flexibility:
- Heat Dissipation:
- Power Transmission Capacity:
- Noise and Vibration:
- Application Suitability:
Standard V-belts have a smooth, continuous surface on the inside, which comes in contact with the pulleys. On the other hand, cogged V-belts have notches or cogs on the inside surface. These cogs allow the belt to flex more easily and improve its flexibility and bending capabilities.
The presence of cogs in cogged V-belts makes them more flexible compared to standard V-belts. This increased flexibility allows cogged V-belts to bend and wrap around smaller pulleys more easily. It also reduces the bending stress and heat generation, resulting in improved performance and longer belt life.
Cogged V-belts have better heat dissipation properties compared to standard V-belts. The cogs create additional surface area, which improves airflow and heat dissipation during operation. This helps to reduce heat buildup and minimize the risk of belt slippage or premature wear due to excessive heat.
Standard V-belts and cogged V-belts have similar power transmission capacity for most applications. However, cogged V-belts may have a slightly reduced power capacity compared to standard V-belts due to the presence of cogs, which can reduce the contact area with the pulleys. As a result, cogged V-belts are typically used in applications that require moderate power transmission.
Cogged V-belts generally produce less noise and vibration compared to standard V-belts during operation. The presence of cogs helps to reduce the vibration and noise caused by belt slippage or engagement with the pulleys. This makes cogged V-belts suitable for applications where noise reduction is important, such as in HVAC systems or household appliances.
Standard V-belts are commonly used in a wide range of industrial applications for power transmission. They are suitable for applications with larger pulleys and higher power requirements. Cogged V-belts, on the other hand, are often preferred in applications that involve smaller pulleys, tighter spaces, or where improved flexibility and reduced noise are desired.
It’s important to consider the specific requirements of the application and consult the manufacturer’s recommendations when choosing between standard V-belts and cogged V-belts. Understanding the key differences between these two types of belts can help in selecting the most appropriate option for a particular power transmission application.

What are the key differences between V-belts and other types of power transmission belts?
V-belts are a popular type of power transmission belts, but they differ from other types of belts in terms of design, construction, and specific applications. Here are the key differences:
1. Belt Profile:
V-belts have a trapezoidal or V-shaped cross-sectional profile, which gives them their name. This profile allows the belts to fit securely into V-shaped pulleys, providing effective power transmission and grip. Other types of belts, such as flat belts or timing belts, have different profiles suited for specific applications.
2. Power Transmission Method:
V-belts transmit power through frictional forces between the belt and the pulleys. As the belt wraps around the pulleys, the friction between the belt and the pulley surfaces allows the transfer of torque and power. In contrast, other belts, like timing belts or chain drives, use toothed profiles or interlocking mechanisms to transmit power, providing precise synchronization and higher torque transmission.
3. Load Capacity:
V-belts are designed to handle moderate to high loads, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, certain applications with heavier loads may require specialized heavy-duty V-belts or alternative belt types, such as synchronous belts or chain drives, which offer higher load-carrying capacities.
4. Speed Range:
V-belts are suitable for a broad speed range, but their limitations may vary depending on the specific design, material, and construction. Traditional V-belts may have speed limitations at extremely high speeds due to centrifugal forces and heat generation. High-speed V-belts or narrow V-belts are available for applications that require higher speeds. In contrast, timing belts and synchronous belts are designed for precise speed control and are commonly used in applications with strict speed requirements.
5. Tensioning and Maintenance:
V-belts require periodic tensioning to maintain proper grip and power transmission efficiency. Tensioning is typically achieved through manual adjustment or automatic tensioners. Other types of belts, such as timing belts or chain drives, often have fixed tensioning systems and require less frequent maintenance.
6. Noise and Vibration:
V-belts generally operate with lower noise and vibration levels compared to other types of belts, such as chain drives. The design and frictional nature of V-belts contribute to smoother operation and reduced noise generation, making them suitable for applications where noise and vibration control is important.
7. Applications:
V-belts are widely used in various applications, including industrial machinery, automotive systems, HVAC systems, and power transmission in general. They are versatile and can accommodate different power requirements. Other belt types, such as timing belts, are commonly used in precision positioning, robotics, or applications that require synchronous motion.
Overall, V-belts offer reliable and cost-effective power transmission for a wide range of applications. However, the selection of the appropriate belt type depends on factors such as load requirements, speed range, precision, noise considerations, and specific application needs.

What is a V-belt and how does it work?
A V-belt, also known as a Vee belt or a wedge belt, is a type of power transmission belt that is commonly used in various industrial applications. It is called a V-belt because of its trapezoidal cross-sectional shape, resembling the letter “V.”
The primary purpose of a V-belt is to transmit power between two rotating shafts. It does this by wrapping around the pulleys or sheaves on the shafts and creating frictional forces between the belt and the pulleys. The friction generated between the belt and the pulleys allows the belt to transfer torque from the driving pulley to the driven pulley.
The V-belt’s design provides several advantages for power transmission:
- High friction: The V-shaped cross-section of the belt increases the contact area with the pulleys, resulting in high frictional forces. This allows for effective power transmission even in applications with high torque or heavy loads.
- Belt wedging: When the V-belt is tensioned, it wedges itself deeper into the pulley grooves, enhancing the friction and preventing slippage between the belt and the pulleys. This feature is especially useful in applications where the driven pulley needs to rotate at a different speed than the driving pulley.
- Quiet operation: V-belts generally operate with less noise compared to other types of belts, such as flat belts. The V-shaped design helps to reduce vibrations and noise levels during power transmission.
- Simple installation: V-belts are relatively easy to install and replace. They can be quickly mounted on the pulleys without requiring extensive alignment procedures.
However, it’s important to note that V-belts have limitations as well. They are not suitable for applications that require precise speed control or when high-speed ratios are needed. In such cases, other power transmission methods like gear systems or synchronous belts may be more appropriate.
In summary, V-belts are commonly used power transmission belts that utilize frictional forces to transfer torque between rotating shafts. Their V-shaped design and high friction characteristics make them effective for various industrial applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-02
China wholesaler Automobile Fan Belt Engine Poly V Belt Dongil CZPT Pk V Ribbed Serpentine Belts a 3-axle vehicle
Product Description
Product Description
Property
— Excellent flexibility
— High power transmission efficiency
— Reduced noise
— a power transmission belt featuring multiple longitudinal ribs.
— It transmits the torque by contact of the belt rib flanks and the pulley grooves.
— It has been designed with a larger contact surface area than V belts or flat belts.
Property
— Smooth running
— More power in less space
— Friction and wedge advantages for v ribbed section
Property
— High grade engineered rubber
— Longer service life
— Temperature range from -50ºC to +120ºC
— Oil, heat,ozone and abrasion resistant
Specification
| Profile | Pb | h | a° |
| H | 1.6 | 3 | 40 |
| J | 2.34 | 4 | 40 |
| K | 3.56 | 6 | 40 |
| L | 4.7 | 10 | 40 |
| M | 9.4 | 17 | 40 |
Production & Package
Forming and coiling process Vulcanizing process
Grinding process Cardbox package
Applications
Company Information
FAQ
Q1. Can I have a sample order for PK belt?
Yes, we welcome sample order to test and check quality. Mixed samples are acceptable.
Q2. What about the lead time?
1) 2–3 days for sample
2) 20–30 days for mass production. If urgent,we have green channel.
Q3. Do you have any MOQ limit for PK belt order?
Low MOQ, 1pc for sample checking is available
Q4. Is it OK to print my logo on V belt product?
Yes. Please inform us your logo or design before mass production
Q5. How to guarantee your quality?
We are 1 of the top suppliers of International famous Belt company over years. Excellent quality is well accepted.
Please contact us for more details.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyer Equipment, Packaging Machinery, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Food Machinery, Marine, Mining Equipment, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
| Feature: | Flame-Retardant, Anti-Static, Oil-Resistant, Cold-Resistant, Corrosion-Resistant, Heat-Resistant, Alkali-Resistant, Skid-Resistance, Wear-Resistant, Acid-Resistant, High Temperature-Resistance |
| Tensile Strength: | Strong |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Type: | Traction Belt |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the key differences between standard V-belts and cogged V-belts?
Standard V-belts and cogged V-belts are two variations of V-belts that differ in their design and performance characteristics. Here are the key differences between these two types of belts:
- Design:
- Flexibility:
- Heat Dissipation:
- Power Transmission Capacity:
- Noise and Vibration:
- Application Suitability:
Standard V-belts have a smooth, continuous surface on the inside, which comes in contact with the pulleys. On the other hand, cogged V-belts have notches or cogs on the inside surface. These cogs allow the belt to flex more easily and improve its flexibility and bending capabilities.
The presence of cogs in cogged V-belts makes them more flexible compared to standard V-belts. This increased flexibility allows cogged V-belts to bend and wrap around smaller pulleys more easily. It also reduces the bending stress and heat generation, resulting in improved performance and longer belt life.
Cogged V-belts have better heat dissipation properties compared to standard V-belts. The cogs create additional surface area, which improves airflow and heat dissipation during operation. This helps to reduce heat buildup and minimize the risk of belt slippage or premature wear due to excessive heat.
Standard V-belts and cogged V-belts have similar power transmission capacity for most applications. However, cogged V-belts may have a slightly reduced power capacity compared to standard V-belts due to the presence of cogs, which can reduce the contact area with the pulleys. As a result, cogged V-belts are typically used in applications that require moderate power transmission.
Cogged V-belts generally produce less noise and vibration compared to standard V-belts during operation. The presence of cogs helps to reduce the vibration and noise caused by belt slippage or engagement with the pulleys. This makes cogged V-belts suitable for applications where noise reduction is important, such as in HVAC systems or household appliances.
Standard V-belts are commonly used in a wide range of industrial applications for power transmission. They are suitable for applications with larger pulleys and higher power requirements. Cogged V-belts, on the other hand, are often preferred in applications that involve smaller pulleys, tighter spaces, or where improved flexibility and reduced noise are desired.
It’s important to consider the specific requirements of the application and consult the manufacturer’s recommendations when choosing between standard V-belts and cogged V-belts. Understanding the key differences between these two types of belts can help in selecting the most appropriate option for a particular power transmission application.

Are there any safety considerations when working with V-belts?
Working with V-belts involves certain safety considerations to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the belt drive system. Here are some important safety considerations when working with V-belts:
- Lockout/Tagout: Before performing any maintenance or adjustment on a belt drive system, it is crucial to follow proper lockout/tagout procedures. Lockout/tagout involves isolating the power source, de-energizing the equipment, and securing it with locks or tags to prevent unintentional startup or release of stored energy. This ensures the safety of personnel working on or near the V-belts.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with V-belts, appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn as per the specific tasks and potential hazards. This may include safety glasses, gloves, hearing protection, and protective clothing to safeguard against potential injury from flying debris, pinch points, or contact with rotating parts.
- Training and Familiarity: Ensure that personnel working with V-belts are adequately trained on safe work practices, including proper maintenance procedures, tensioning techniques, and the use of tools and equipment. Familiarity with the specific belt drive system and understanding the potential hazards associated with V-belts is essential for safe operation.
- Machine Guarding: Install appropriate machine guarding to prevent accidental contact with moving V-belts and exposed pulleys. Guards should be designed to prevent access to hazardous areas and comply with relevant safety regulations. Regularly inspect and maintain the guards to ensure their effectiveness.
- Tensioning and Adjustment: Follow proper procedures when tensioning or adjusting V-belts. Use the recommended tools and techniques specified by the manufacturer. Improper tensioning can lead to belt slippage, increased wear, and potential accidents. Avoid working near or reaching into the belt drive system while it is in operation.
- Proper Lifting and Handling: V-belts can be heavy and awkward to handle, especially in larger sizes. When lifting or handling V-belts, use proper lifting techniques and equipment to prevent strains or injuries. Avoid placing excessive stress on the belts during installation or removal.
- Maintaining Cleanliness: Keep the work area clean and free from debris, oil, or other contaminants that may affect traction or create slip hazards. Clean up any spills promptly and use appropriate cleaning methods to avoid slipping or tripping accidents.
- Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and specifications for the installation, tensioning, maintenance, and replacement of V-belts. Manufacturers provide valuable information on safe operating practices, recommended tension ranges, load capacities, and other relevant safety considerations specific to their V-belt products.
By following these safety considerations when working with V-belts, you can help mitigate potential hazards, reduce the risk of accidents, and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the belt drive system.

How do you measure and select the right size of V-belt for a specific application?
When selecting the right size of V-belt for a specific application, it is important to consider factors such as the pulley diameters, center distance between the pulleys, power requirements, and the desired operating speed. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to measure and select the appropriate V-belt size:
- Identify the pulley diameters: Measure the diameter of both the driving and driven pulleys. Make sure to measure the diameter at the highest point of the pulley groove where the belt rides.
- Determine the center distance: Measure the distance between the center points of the driving and driven pulleys. This is the center distance and it plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate V-belt length.
- Calculate the pitch diameter: The pitch diameter is the effective diameter where the belt contacts the pulley. It can be calculated using the following formula: Pitch Diameter = (Driving Pulley Diameter + Driven Pulley Diameter) / 2.
- Consider the power requirements: Determine the amount of power that needs to be transmitted by the V-belt. This can be in the form of horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or engineering specifications to ensure the selected V-belt can handle the required power.
- Choose the appropriate V-belt type: Based on the calculated pitch diameter, center distance, and power requirements, select the type of V-belt that is suitable for the specific application. Consider factors such as load capacity, speed capability, and environmental conditions.
- Refer to V-belt manufacturer’s catalogs: Consult the manufacturer’s catalogs or online resources to find the available V-belt sizes and corresponding part numbers. Cross-reference the calculated parameters with the provided charts or tables to identify the appropriate V-belt size.
- Verify the selection: Double-check the selected V-belt size against the calculated parameters to ensure accuracy. If possible, consult with a technical expert or the manufacturer’s support team to validate the selection.
It is important to note that V-belt sizes are standardized and typically follow specific designations, such as the Classical V-belt designation (e.g., A, B, C, D) or the metric designation (e.g., SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC). These designations indicate different belt widths and lengths.
In summary, measuring and selecting the right size of V-belt for a specific application involves identifying the pulley diameters, determining the center distance, calculating the pitch diameter, considering the power requirements, choosing the appropriate V-belt type, referring to manufacturer’s catalogs, and verifying the selection. Following these steps will help ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the V-belt in the intended application.


editor by CX 2024-05-02
China wholesaler Auto Parts Engine Timing Belt 25212-03980 V-Ribbed Belt for 9pk 1227 Korean Cars 2521203980 axle cap
Product Description
Key attributes
| OE NO. | 25212- 0571 0 |
Basic Information :
| OE NO. | 25212- 0571 0 | Product name | Engine Timing Belt |
| Type | Timing Belt | Warranty | 12 Months |
| Brand Name | C&Z | Place of Origin | HangZhou, China |
| Size | STD | MOQ | 10pcs |
| Type | Speed sensor | Application | Hyundai;Kia |
| Packing | Carton Box | DELIVERY TIME | 10-30 Days |
| Port | HangZhou | Supply Ability | 2000 Piece/Pieces per Month |
Our Servic :
As a senior auto parts manufacturer, we have a professional QC team with the strong sense of responsibility. We maintain tight control over every detail to ensure the quality of each batch of products. Every working procedure is monitored by our specialists to ensure the best quality. We will try our utmost to provide professional services to help our clients keep ahead of competition,achieve maximum benefits and enjoy reliable after service. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them, no matter where they come from.
What others we supply for Hyundai KIA :
| Engine parts | Valve chamber cover system and oil pan |
| Engine timing belt | |
| Timing chain kit | |
| Oil pumps | |
| Engine water pump | |
| Full gasket set | |
| Oil Dipstick | |
| Chassis parts | Suspension system |
| Tie rd ends | |
| Ball joints | |
| Stabilizer link | |
| Wheel hub bearing | |
| Electrical parts | Trunk release switch |
| Wheel speed sensor cover | |
| Cooling system | |
| Transmission system | |
| Ungrouped | |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 2 Year After Selling Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Car Make: | Hyundai KIA |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Are there any specific guidelines for aligning pulleys and V-belts?
Proper alignment between pulleys and V-belts is essential to ensure smooth operation, minimize wear, and maximize the efficiency of the belt drive system. Here are some specific guidelines for aligning pulleys and V-belts:
- Parallel Alignment:
- Angular Alignment:
- Alignment Tools:
- Adjustment Methods:
- Regular Inspections:
- Manufacturer Recommendations:
The pulleys should be aligned parallel to each other, meaning that the axes of the pulleys should be in the same plane. This ensures that the V-belt runs straight and evenly between the pulleys. Misalignment can cause the belt to run at an angle, leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency.
In addition to parallel alignment, the pulleys should be aligned angularly. This means that the pulley faces should be perpendicular to the belt’s direction of travel. Angular misalignment can cause the belt to twist and create uneven tension, resulting in increased wear and potential belt failure.
To achieve proper alignment, various alignment tools can be used, such as straightedges, laser alignment tools, or alignment software. These tools help in measuring and adjusting the alignment of pulleys, ensuring precise parallel and angular alignment.
To adjust the alignment of pulleys, different methods can be employed. Common adjustment methods include shimming, moving the pulley on its shaft, or using adjustable pulleys. The specific method depends on the type of pulley and the adjustment capabilities of the system.
Regular inspections are crucial to identify and correct any misalignment issues promptly. Inspect the pulleys visually and check for any signs of misalignment, such as uneven belt wear, belt tracking issues, or abnormal belt noise. If misalignment is detected, take corrective measures to realign the pulleys.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for pulley alignment. Manufacturers often provide specific alignment tolerances and recommendations for their products, considering factors such as belt type, load, and operating conditions. Follow these recommendations to ensure proper alignment and optimize the performance of the belt drive system.
By following these guidelines for aligning pulleys and V-belts, you can minimize wear, reduce the risk of belt failure, and maximize the efficiency and lifespan of the belt drive system.

What are the key differences between V-belts and other types of power transmission belts?
V-belts are a popular type of power transmission belts, but they differ from other types of belts in terms of design, construction, and specific applications. Here are the key differences:
1. Belt Profile:
V-belts have a trapezoidal or V-shaped cross-sectional profile, which gives them their name. This profile allows the belts to fit securely into V-shaped pulleys, providing effective power transmission and grip. Other types of belts, such as flat belts or timing belts, have different profiles suited for specific applications.
2. Power Transmission Method:
V-belts transmit power through frictional forces between the belt and the pulleys. As the belt wraps around the pulleys, the friction between the belt and the pulley surfaces allows the transfer of torque and power. In contrast, other belts, like timing belts or chain drives, use toothed profiles or interlocking mechanisms to transmit power, providing precise synchronization and higher torque transmission.
3. Load Capacity:
V-belts are designed to handle moderate to high loads, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, certain applications with heavier loads may require specialized heavy-duty V-belts or alternative belt types, such as synchronous belts or chain drives, which offer higher load-carrying capacities.
4. Speed Range:
V-belts are suitable for a broad speed range, but their limitations may vary depending on the specific design, material, and construction. Traditional V-belts may have speed limitations at extremely high speeds due to centrifugal forces and heat generation. High-speed V-belts or narrow V-belts are available for applications that require higher speeds. In contrast, timing belts and synchronous belts are designed for precise speed control and are commonly used in applications with strict speed requirements.
5. Tensioning and Maintenance:
V-belts require periodic tensioning to maintain proper grip and power transmission efficiency. Tensioning is typically achieved through manual adjustment or automatic tensioners. Other types of belts, such as timing belts or chain drives, often have fixed tensioning systems and require less frequent maintenance.
6. Noise and Vibration:
V-belts generally operate with lower noise and vibration levels compared to other types of belts, such as chain drives. The design and frictional nature of V-belts contribute to smoother operation and reduced noise generation, making them suitable for applications where noise and vibration control is important.
7. Applications:
V-belts are widely used in various applications, including industrial machinery, automotive systems, HVAC systems, and power transmission in general. They are versatile and can accommodate different power requirements. Other belt types, such as timing belts, are commonly used in precision positioning, robotics, or applications that require synchronous motion.
Overall, V-belts offer reliable and cost-effective power transmission for a wide range of applications. However, the selection of the appropriate belt type depends on factors such as load requirements, speed range, precision, noise considerations, and specific application needs.

What are the common causes of V-belt failure and how can they be prevented?
V-belt failure can occur due to various factors, and understanding the common causes is essential for preventing premature belt failure and ensuring reliable operation. Here are some common causes of V-belt failure and preventive measures:
- Misalignment: Misalignment between the pulleys can cause excessive wear, uneven load distribution, and belt slippage. To prevent misalignment, ensure proper pulley alignment during installation and regularly inspect and adjust the pulleys as needed.
- Over-tensioning or under-tensioning: Incorrect belt tension can lead to excessive stress or slippage. Over-tensioning can cause accelerated wear, while under-tensioning can result in belt slipping and reduced power transmission. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended tension guidelines and use a tension gauge to achieve the proper tension for the specific V-belt.
- Pulley damage: Damaged or worn-out pulleys can cause belt damage and premature failure. Inspect the pulleys regularly for signs of wear, such as grooves, cracks, or deformation. Replace any damaged pulleys promptly to prevent belt damage.
- Contamination: Contaminants such as dirt, debris, oil, or chemicals can affect the belt’s grip and cause accelerated wear. Keep the belt and pulleys clean and free from contaminants. Regularly inspect the environment and implement appropriate measures to prevent contamination.
- Excessive heat: High temperatures can cause belt degradation, leading to reduced strength and increased wear. Ensure proper ventilation and cooling in the belt drive system. If the application generates excessive heat, consider using heat-resistant belts or implementing cooling measures.
- Excessive load: Overloading the V-belt beyond its capacity can cause excessive stress and lead to premature failure. Ensure the V-belt is appropriately sized for the application and consider factors such as torque, horsepower, and load requirements. If the load exceeds the belt’s capacity, consider using a higher-rated belt or alternative power transmission methods.
- Age and wear: Over time, V-belts naturally wear out and lose their effectiveness. Regularly inspect the belts for signs of wear, such as fraying, cracking, or glazing. Replace worn-out belts as part of a preventive maintenance schedule to avoid unexpected failures.
Preventive measures to reduce V-belt failure include regular inspections, proper installation, correct tensioning, pulley maintenance, cleanliness, temperature management, load monitoring, and timely replacement. Following manufacturer’s guidelines, conducting routine maintenance, and addressing any issues promptly will help extend the lifespan and reliability of V-belts in power transmission systems.
In summary, common causes of V-belt failure include misalignment, incorrect tensioning, pulley damage, contamination, excessive heat, excessive load, and age/wear. By implementing preventive measures and conducting regular maintenance, these causes can be minimized, ensuring optimal V-belt performance and longevity.


editor by CX 2024-04-30
China Good quality Xpa1090 Toothed Triangle Belts/Super Tx Vextra V-Belts/High Temperature Timing Belts with Good quality
Product Description
XPA1090 Toothed Triangle Belts/Super TX Vextra V-Belts/High Temperature Timing Belts
There’s 556 pcs of XPA1090 belts are available in stock now, you can send me an email or Skype messages or What’sapp
messages to contact me if want to order or consult information of XPA1090 belts, the prompt response, competitive prices,
superior quality and service are waiting for you.
The detailed technical sheet of XPA1090 belts as follows:
| Model | XPA1090 | |
| Type | V-belts | |
| Description | Toothed Triangle Belts/Super TX Vextra Belts/High Temperature Timing Belts | |
| mass | 0.2 KG | |
| Service | Neutral/OEM/As per your request | |
| Package | Carton Box | |
| Stock Qty | 556 pcs | |
| Country of Origin | USA/Germany/Japan | |
| HS Code | 4571390000 | |
Wanna more information of XPA1090 belts, or still sourcing any other bearings, linear blocks/rails, industrial V-belts or sparg plugs,
just contact me now.
In addition, the following V-belts are available now, pls feel free to let me know if you’re interested in it:
XPA series of toothed V-belt
XPA732 , XPA747 , XPA757 , XPA770 , XPA782 , XPA800 , XPA810 , XPA820 , XPA832 ,XPA850 , XPA857 , XPA882 , XPA900 , XPA907 , XPA925 , XPA932 , XPA950 , XPA957 ,XPA975 , XPA982 , XPA1000 , XPA1007 , XPA1030 , XPA1060 , XPA1080 , XPA1090 ,XPA1107 , XPA1120 , XPA1132 , XPA1140 , XPA1150 , XPA1157 , XPA1180 , XPA1207 , XPA1215 , XPA1232 , XPA1250 , XPA1272 , XPA1282 , XPA1307 , XPA1320 , XPA1332 , XPA1357 , XPA1382 , XPA1400 , XPA1407 , XPA1432 , XPA1450 , XPA1457 , XPA1482 , XPA1500 , XPA1500 , XPA1507 , XPA1532 , XPA1550 , XPA1557 , XPA1582 , XPA1600 , XPA1607 , XPA1632 , XPA1650 , XPA1657 , XPA1682 , XPA1700 , XPA1732 , XPA1750 , XPA1757 , XPA1782 , XPA1800 , XPA1807 , XPA1832 , XPA1850 , XPA1857 , XPA1882 , XPA1900 , XPA1907 , XPA1932 , XPA1950 , XPA1957 , XPA1982 , XPA2000 , XPA2032 , XPA2060 , XPA2082 , XPA2120 , XPA2132 , XPA2182 , XPA2240 , XPA2282 , XPA2300 , XPA2332 , XPA2360 , XPA2382 , XPA2430 , XPA2482 , XPA2500 , XPA2532 , XPA2582 , XPA2607 , XPA2632 , XPA2650 , XPA2682 , XPA2732 , XPA2782 , XPA2800 , XPA2832 , XPA2847 , XPA2882 , XPA2900 , XPA2932 , XPA2982 , XPA3000 , XPA3150 , XPA3350 , XPA3550
XPB series of toothed V-belt
XPB1130 , XPB1180 , XPB1230 , XPB1250 , XPB1260 , XPB1280 , XPB1320 , XPB1340 , XPB1360 , XPB1380 , XPB1400 , XPB1410 , XPB1430 , XPB1460 , XPB1480 , XPB1500 , XPB1510 , XPB1540 , XPB1590 , XPB1600 , XPB1640 , XPB1660 , XPB1690 , XPB1700 , XPB1720 , XPB1740 , XPB1800 , XPB1840 , XPB1870 , XPB1900 , XPB2000 , XPB2571 , XPB2040 , XPB2100 , XPB2120 , XPB2150 , XPB2160 , XPB2170 , XPB2220 , XPB2240 , XPB2280 , XPB2350 , XPB2360 , XPB2380 , XPB2410 , XPB2430 , XPB2500 , XPB2530 , XPB2600 , XPB2650 , XPB2680 , XPB2730 , XPB2800 , XPB2840 , XPB2910 , XPB2990 , XPB3000 , XPB3110 , XPB3150 , XPB3170 , XPB3340 , XPB3550
XPC series of toothed V-belt
XPC2000, XPC2120, XPC2240, XPC2360, XPC2500 ,XPC2650, XPC2800XPC3000, XPC3150, XPC3350, XPC3550, XPC3750 ,XPC4000 ,XPC4250, XPC4500 XPC4750
XPZ series of toothed V-belt
XPZ560 ,XPZ612 ,XPZ621 ,XPZ630 ,XPZ637 ,XPZ662 ,XPZ670 ,XPZ687 ,XPZ710,XPZ722 ,XPZ730 ,XPZ737 ,XPZ750 ,XPZ760 ,XPZ762 ,XPZ772 ,XPZ787 ,XPZ800,XPZ812 ,XPZ825 ,XPZ837 ,XPZ850 ,XPZ862 ,XPZ875 ,XPZ887 ,XPZ900 ,XPZ912,XPZ925 ,XPZ937 ,XPZ950 ,XPZ962 ,XPZ975 ,XPZ987 ,XPZ1000 ,XPZ1571 , XPZ1012 , XPZ1571 , XPZ1030 , XPZ1037 , XPZ1047 , XPZ1060 , XPZ1077 , XPZ1080 , XPZ1087 , XPZ1100 , XPZ1112 , XPZ1120 , XPZ1140 , XPZ1150 , XPZ1162 , XPZ1180 , XPZ1187 , XPZ1200 , XPZ1212 , XPZ1222 , XPZ1237 , XPZ1250 , XPZ1262 , XPZ1270 , XPZ1287 , XPZ1312 , XPZ1320 , XPZ1337 , XPZ1340 , XPZ1347 , XPZ1362 , XPZ1387 , XPZ1400 , XPZ1412 , XPZ1420 , XPZ1437 , XPZ1450 , XPZ1462 , XPZ1487 , XPZ1500 , XPZ1512 , XPZ1520 , XPZ1537 , XPZ1550 , XPZ1562 , XPZ1587 , XPZ1600 , XPZ1612 , XPZ1637 , XPZ1650 , XPZ1662 , XPZ1687 , XPZ1700 , XPZ1737 , XPZ1750 , XPZ1762 , XPZ1782 , XPZ1800 , XPZ1812 , XPZ1837 , XPZ1850 , XPZ1862 , XPZ1887 , XPZ1900 , XPZ1937 , XPZ1950 , XPZ1987 , XPZ2000 , XPZ2030 , XPZ2060 , XPZ2120 , XPZ2160 , XPZ2240 , XPZ2280 , XPZ2360 , XPZ2410 , XPZ2487 , XPZ2500 , XPZ2540 , XPZ2650 , XPZ2690 , XPZ2840 , XPZ3000 , XPZ3170 , XPZ3350 , XPZ3550
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyer Equipment, Packaging Machinery, Food Machinery, Marine, Mining Equipment |
| Feature: | Anti-Static, Oil-Resistant, Cold-Resistant, Corrosion-Resistant, Heat-Resistant, High Temperature-Resistance |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Are there any alternatives to V-belts for power transmission applications?
Yes, there are several alternatives to V-belts for power transmission applications. These alternatives offer different advantages and may be suitable for specific requirements. Here are some commonly used alternatives:
- Synchronous Belts:
- Flat Belts:
- V-Ribbed Belts:
- Chain Drives:
- Gear Drives:
- Direct Coupling:
Synchronous belts, also known as timing belts, are toothed belts that provide precise and synchronous power transmission. They have teeth on the inner side that mesh with corresponding grooves on the pulleys, eliminating slippage and ensuring accurate power transfer. Synchronous belts are commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, high torque transmission, or low maintenance.
Flat belts are thin, flexible belts that transmit power by friction between the belt and the pulleys. They offer a simple and cost-effective solution for power transmission. Flat belts are available in various materials, such as rubber, leather, or fabric-reinforced synthetic materials. They are suitable for applications with moderate power requirements and can be used in both light-duty and heavy-duty applications.
V-ribbed belts, also known as multi-rib belts or serpentine belts, are similar to V-belts but have a different cross-sectional shape. They have a flat or shallow V-shaped profile with ribs on the inner side, which engage with corresponding grooves on the pulleys. V-ribbed belts offer higher power transmission capacity and reduced slip compared to standard V-belts. They are commonly used in automotive applications, such as engine accessory drives.
Chain drives use a series of interconnected links to transmit power. They are known for their high strength, durability, and ability to handle heavy loads. Chain drives are commonly used in applications that require high torque transmission, such as industrial machinery, motorcycles, or bicycles. However, chain drives require periodic lubrication and maintenance to ensure proper operation.
Gear drives utilize interlocking gears to transmit power. They offer high efficiency, precise power transmission, and the ability to transmit large amounts of torque. Gear drives are commonly used in applications that require high precision, such as robotics, machine tools, or automotive transmissions. However, they can be more complex and expensive compared to belt drives.
In some cases, power transmission applications may utilize direct coupling, where the motor shaft is directly connected to the driven equipment without the use of belts or other intermediate components. Direct coupling offers high efficiency, compactness, and eliminates the need for belt maintenance. It is commonly used in applications with high torque requirements or where precise alignment is critical.
The choice of the alternative to V-belts depends on various factors, including the specific power transmission requirements, space limitations, cost considerations, maintenance needs, and the desired level of precision. It is important to evaluate these factors and consult with experts to select the most suitable alternative for a particular application.

How do you troubleshoot common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing?
Troubleshooting common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing, is essential to maintain the proper operation and efficiency of the belt drive system. Here are some troubleshooting steps to address these issues:
- Slipping:
- Check the belt tension: Insufficient tension is a common cause of slipping. Ensure that the V-belt is properly tensioned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Adjust the tension by using the appropriate tensioning method or tools.
- Inspect for wear or damage: Examine the V-belt for signs of wear, cracks, fraying, or other damage. A worn-out belt may not provide adequate grip and can lead to slipping. Replace the belt if necessary.
- Check pulley alignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to slip. Verify that the pulleys are properly aligned both parallel and angularly. Adjust the pulley positions if misalignment is detected.
- Assess pulley condition: Worn or damaged pulleys can contribute to belt slipping. Inspect the pulleys for wear, rough surfaces, or damage. If needed, replace the pulleys to ensure proper belt engagement.
- Verify the load and application: Excessive loads or improper application can cause the belt to slip. Ensure that the belt drive system is designed and rated for the specific load requirements.
- Squealing:
- Check belt tension: Insufficient or excessive belt tension can lead to squealing. Adjust the tension to the recommended range specified by the manufacturer.
- Inspect for wear or contamination: Check the V-belt for signs of wear, glazing, or contamination. Worn or contaminated belts may produce squealing noises. Replace the belt if necessary and eliminate any contamination from the belt or pulleys.
- Examine pulley condition: Damaged or worn pulleys can create noise. Inspect the pulleys for wear, damage, or rough surfaces. Replace any worn or damaged pulleys.
- Verify pulley alignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to run at an angle, resulting in noise. Ensure that the pulleys are correctly aligned both parallel and angularly. Adjust the pulley positions if misalignment is detected.
- Check for belt glazing: Belt glazing occurs when the belt’s contact surface becomes smooth and glossy, reducing traction. If glazing is present, roughen the belt’s surface with fine sandpaper or replace the belt if necessary.
- Assess environmental factors: Environmental conditions, such as excessive heat or humidity, can affect belt performance. Ensure that the belt drive system operates within the recommended temperature and humidity ranges.
Slipping occurs when the V-belt fails to maintain proper traction with the pulleys, resulting in reduced power transmission and potential belt wear. To troubleshoot slipping issues:
Squealing noises from V-belts are often caused by vibrations, misalignment, or improper tension. To troubleshoot squealing issues:
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can identify and address common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing. Regular maintenance, proper tensioning, and alignment are crucial for ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of the belt drive system.

What are the advantages of using V-belts in power transmission systems?
V-belts offer several advantages when used in power transmission systems:
- High friction: The V-shaped cross-section of the belt increases the contact area with the pulleys, resulting in high frictional forces. This allows for effective power transmission even in applications with high torque or heavy loads.
- Belt wedging: When the V-belt is tensioned, it wedges itself deeper into the pulley grooves, enhancing the friction and preventing slippage between the belt and the pulleys. This feature is especially useful in applications where the driven pulley needs to rotate at a different speed than the driving pulley.
- Quiet operation: V-belts generally operate with less noise compared to other types of belts, such as flat belts. The V-shaped design helps to reduce vibrations and noise levels during power transmission.
- Simple installation: V-belts are relatively easy to install and replace. They can be quickly mounted on the pulleys without requiring extensive alignment procedures.
- Cost-effective: V-belts are typically more affordable compared to other power transmission methods, such as gear systems or synchronous belts. This makes them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
- Flexibility: V-belts can accommodate misalignments and slight variations in pulley diameters. They can also operate in a wide range of temperature and humidity conditions, making them versatile for different environments.
- Energy efficiency: V-belts have relatively low energy losses during power transmission, resulting in efficient energy transfer between the driving and driven pulleys.
It’s important to note that while V-belts offer numerous advantages, they also have limitations. They are not suitable for applications that require precise speed control or when high-speed ratios are needed. In such cases, other power transmission methods may be more appropriate.
In conclusion, the advantages of using V-belts in power transmission systems include high friction, belt wedging, quiet operation, simple installation, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and energy efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-04-30
China high quality Sidewall Conveyor Belt V Belt Transmission Crusher Mesh Conveyor Belt for Sale manufacturer
Product Description
Product Description
Sidewall Conveyor Belt V Belt Transmission Crusher Mesh Conveyor Belt for sale
It is widely use in many fields like the following:
1.Applications: The steel cord conveyor belt is widely used in distributed occasions ,such as cement industry, coal mines, quarries, mining, electric power Plants, metallurgic industry, ports and chemical industry, etc.
2.Advantages:The belt has properties of high tensile strength, low elongation, impact resistance and good trough ability. It’s available for long-distance,
Large-capacity and high-speed transportation of materials.
3.Better flexure than multi-ply fabric belt with the same strength; smaller diameters for the required pulley.
4.Using galvanized open steel cords and rubber materials with a property of good adhesion, which creates a good combination between the steel and the core
Rubber .And the belt can show good impact resistance and have a long working life.
5.With advanced manufacturing techniques, steel cords are evenly arranged with the same tension,Therefore, the belt can run well and avoid drift.
6.One or 2 layers of anti-tear materials are added to the products according to customers’ special requests in order to decrease the possibilities of tear
Within longitudinal range.
Product Parameters
|
Technical Data |
ST/S 630 | ST/S 865286925 /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
What are the best practices for storing spare V-belts to maintain their quality?Proper storage of spare V-belts is essential to maintain their quality and ensure their performance when they are needed. Here are some best practices for storing spare V-belts:
Store the V-belts in a clean and dry environment to prevent contamination and moisture damage. Avoid storing them in areas where they may be exposed to dirt, dust, chemicals, or excessive humidity. Keeping the storage area clean and well-ventilated helps preserve the integrity of the belts. Ensure that the storage area has controlled temperature and humidity levels. Extreme temperatures or high humidity can adversely affect the belt material, leading to deterioration or loss of elasticity. Ideally, the temperature should be kept within a range of 10°C to 30°C (50°F to 86°F), and the humidity should be maintained at around 40% to 70%. Direct exposure to sunlight can cause the belt material to degrade over time. Store the spare V-belts away from direct sunlight or any other sources of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. If possible, use opaque containers or covers to shield the belts from light. Do not store the V-belts in a way that causes excessive bending or twisting. This can result in permanent deformation or stress on the belts, compromising their performance. Keep the belts flat or hang them in a manner that maintains their original shape. If the V-belts are stored in packaging, ensure that the packaging is intact and provides adequate protection against external elements. Avoid storing the belts in damaged or torn packaging, as it may expose them to contaminants or moisture. Implement a first-in-first-out (FIFO) rotation system for spare V-belts. This means using the oldest belts first and replenishing the stock with newly purchased belts. This practice helps prevent the storage of belts for extended periods, reducing the risk of degradation or obsolescence. Periodically inspect the stored V-belts for any signs of damage, such as cracks, brittleness, or deterioration. If any issues are detected, replace the affected belts promptly to ensure that only high-quality spare belts are available for use when needed. By following these best practices, you can maintain the quality and performance of spare V-belts, ensuring that they are ready for use and prolonging their service life.
Are there any safety considerations when working with V-belts?Working with V-belts involves certain safety considerations to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the belt drive system. Here are some important safety considerations when working with V-belts:
By following these safety considerations when working with V-belts, you can help mitigate potential hazards, reduce the risk of accidents, and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the belt drive system.
How do you measure and select the right size of V-belt for a specific application?When selecting the right size of V-belt for a specific application, it is important to consider factors such as the pulley diameters, center distance between the pulleys, power requirements, and the desired operating speed. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to measure and select the appropriate V-belt size:
It is important to note that V-belt sizes are standardized and typically follow specific designations, such as the Classical V-belt designation (e.g., A, B, C, D) or the metric designation (e.g., SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC). These designations indicate different belt widths and lengths. In summary, measuring and selecting the right size of V-belt for a specific application involves identifying the pulley diameters, determining the center distance, calculating the pitch diameter, considering the power requirements, choosing the appropriate V-belt type, referring to manufacturer’s catalogs, and verifying the selection. Following these steps will help ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the V-belt in the intended application.
China supplier V Ribbed Belt 3104860 for CZPT Qsx15 Diesel Engine axle alignmentProduct Description
V Ribbed Belt 3104860 for CZPT QSX15 Diesel EngineProduct Description
Detailed Photos More Engine Spare Parts
Company Profile Certifications Our Advantages 1. We have more than 10 years of experience in CZPT diesel engine parts.Especially in PT fuel system parts such as PT injector,PT fuel pump and parts for them. 2. We cooperate with many certificated OEM factories of CZPT who have advanced equipment and technology. 3. We provide a full range of CZPT parts for all CZPT and CZPT engines such as M11,NT855,K19,K38,K50,4BT,6BT,QSB,QSC,ISF,L10,V28,N14,QSX etc. We also have full stock for general parts so we can deliver in a short time. 4. High Quality + Reasonable Price + Quick Response + Technical Support, is what we are trying to offer you the best cooperation experience. FAQ Q1: How to contact you? Q2: Do you have MOQ? Q3:Do you provide sample? Q4: What is the delivery time? Q5: What is the shipping way? Q6:How can I make payment if the order is confirmed? Q7: What is your warranty ? /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
How do you calculate the power rating and speed capacity of a V-belt system?Calculating the power rating and speed capacity of a V-belt system involves considering various factors such as belt type, pulley dimensions, belt tension, and speed. Here’s a general overview of the calculations involved:
To calculate the power rating of a V-belt system, you need to determine the maximum power that the belt can transmit without slipping or experiencing excessive wear. The power rating is typically expressed in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). The formula for calculating the power rating is: Power (HP or kW) = (Tension in belt (lb or N) * Belt speed (ft/min or m/s)) / 33,000 (for HP) or 1,000 (for kW) The tension in the belt can be determined based on the design requirements of the system and is influenced by factors such as the type of application and the desired safety factor. The speed capacity of a V-belt system is the maximum rotational speed at which the belt can operate without experiencing excessive vibration or failure. It is typically expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM). The formula for calculating the speed capacity is: Speed (RPM) = (Belt pitch diameter (in or mm) * π * Belt speed (ft/min or m/s)) / 12 (for in) or 1000 (for mm) The belt pitch diameter is determined based on the pulley dimensions and is the effective diameter at which the belt engages with the pulley. It’s important to note that these calculations provide general guidelines, and actual power rating and speed capacity may vary depending on the specific belt and pulley design, as well as other factors such as belt tensioning, environmental conditions, and system efficiency. It is recommended to consult the belt manufacturer’s guidelines or seek assistance from an engineer experienced in power transmission systems to ensure accurate calculations and appropriate belt selection for a given application.
What are the factors that affect the lifespan and efficiency of V-belts?The lifespan and efficiency of V-belts can be influenced by several factors. Here are the key factors that can affect the performance of V-belts:
Proper belt tension is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of V-belts. Insufficient tension can cause slippage, while excessive tension can lead to excessive load on the belt and other components. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the correct tension range. Poor belt alignment can cause uneven wear, increased friction, and reduced efficiency. Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to run at an angle, resulting in premature wear and potential failure. Regularly check and adjust the alignment of pulleys to ensure proper belt tracking. The condition of the V-belt itself is a significant factor in its lifespan and efficiency. Regularly inspect the belt for signs of wear, cracks, fraying, or glazing. Replace worn-out or damaged belts promptly to avoid further issues. Proper maintenance and lubrication can significantly extend the lifespan of V-belts. Adequate lubrication reduces friction and heat buildup, which helps to prevent premature wear and cracking. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and use the appropriate lubricant. Operating conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals or contaminants, can affect the performance of V-belts. Extreme temperatures can cause the belt material to deteriorate, while exposure to chemicals or contaminants can lead to belt degradation. Ensure that the operating conditions are within the recommended range for the specific V-belt. The load and application requirements also impact the lifespan and efficiency of V-belts. Excessive loads or improper application can cause excessive stress on the belt, leading to premature failure. Ensure that the V-belt is appropriately sized and rated for the specific load and application. By considering these factors and implementing proper maintenance practices, such as regular inspections, correct tensioning, alignment checks, and appropriate lubrication, you can maximize the lifespan and efficiency of V-belts in your applications.
How do you properly install and tension a V-belt for optimal performance?Proper installation and tensioning of a V-belt are crucial for achieving optimal performance and ensuring its longevity. Here are the steps to properly install and tension a V-belt:
It is important to refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications for the specific V-belt type and application. They may provide additional instructions or considerations for installation and tensioning. By following these steps and adhering to the manufacturer’s recommendations, you can ensure the proper installation and tensioning of a V-belt, leading to optimal performance, reduced wear, and extended belt life.
|
